Installting a Node as Azure Container App
Introduction
Beside running the Crosser Node on a stand-alone Docker setup, or using a container orchestration system like Kubernetes/OpenShift, you can also run the Node as an Azure Container App in your Azure infrastructure. This gives you the advantage of not having to deal with overhead like resources and management of an operating system which hosts the Node. In addition, Azure Container Apps allow you to scale the resources of your container in a smooth and easy way making it highly adjustable for your use case.
Prerequisites
The Crosser Node requires persistent local storage which allows the Node to store log files, settings, deployed flows and other things. If you run the Node as an Azure Container App without persistent storage, the Node will run just fine but it will lose all deployed flows with every restart. To avoid that you have to map a persistent File Share into your container.
1. Create File Share
In your Azure portal navigate to Storage Accounts, add a new storage or use an existing one and add a File Share to it.
Keep in mind that every Node will require one unique File Share.

We will need the File Share Name later on, in this case nodecontainerapp.
On your storage account, move to Access keys and show/copy one of the available keys for your storage account.

You will need the Key later on.
2. Create Container App
In your Azure portal, go to Container Apps and click create. Specify the basic settings according to your needs and click Next: Container.
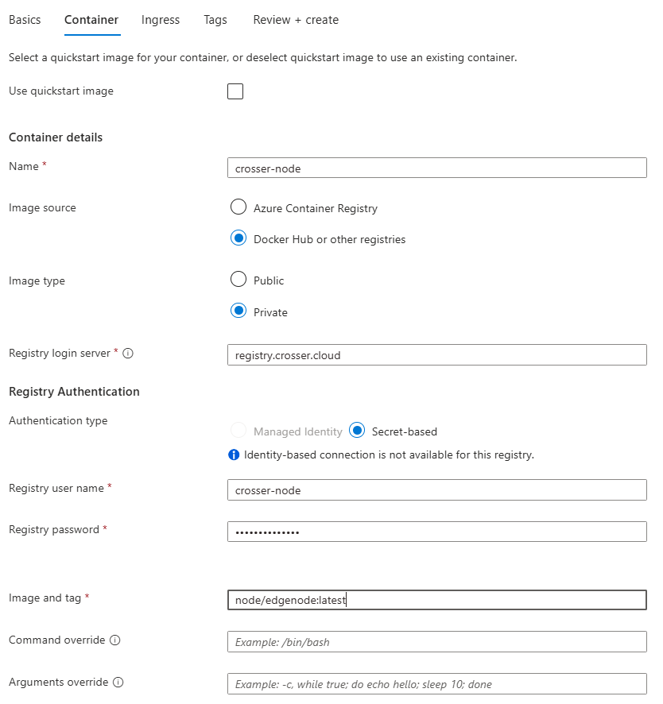
For Environment variables, you have to add at least:
SecurityConfiguration__Credentials__NodeId
SecurityConfiguration__Credentials__AccessKey
NodeID and AccessKey are the Node credentials that you get when creating the Node in your Crosser Control Center organization.
If you want to expose ports from the Node, you can specify the Ingress settings according to your needs. By default the Node comes with a webserver and internal MQTT Broker which allow communication to external services.
Port 9090: Default web server for receiving data in Flows using the HTTP Listener module.
Port 9191: Node web UI and monitoring REST API
Port 1883: MQTT Broker
For our basic setup we do not expose any ports.
Follow the next steps and click create.
3. Configure Container App Environment
Navigate to your Container App Environment -> Settings -> Azure Files.
Add an SMB share with Read/Write permission. Make sure the Share name matches the Share name in your storage account (nodecontainerapp).

4. Configure Container App
4.1 Create volume
Navigate to Application -> Volumes and add the volume that you have added in your Container App Environment (nodecontainerapp)

4.2 Mount volume
Navigate to Application -> Containers and add the volume nodecontainerapp mount to Mount path /application/data.

Now your container should have been restart with a new revision.
5. Verify
To verify that the container is up and running click on Revisions and replicas.

In addition we recommend checking whether or not the Node is shown as online in your Crosser Control Center organization.
Also, once the Node is running, you should find the usual known folder structure in the File share which was added to the Container deployment.

Search Documentation
Page Sections
